- Excel Visual Basic Programming Examples
- Microsoft Excel Visual Basic Reference
- Visual Basic Code Excel Examples
What are Macros?
They are a series of commands used to automate a repeated task. This can be run whenever the task must be performed.
How to access Macros
Click on the ‘View’ tab, at the end you’ll find the function ‘Macros’ arranged in the Macros group. Click the arrow under ‘Macros’ where you can manage your macro performances easily.
To edit a macro, click on the ‘Edit’ button, this will take you to the ‘Visual Basic Editor’ where you can easily modify the macro to do what you want.
Visual Basic Editor view:
10 Useful Examples of Macros for Accounting:
- Excel Macro Examples & Free Downloads One of the best ways to learn Excel VBA is by exploring code samples & examples. That is why, we publish detailed examples, downloadable workbooks & full-length tutorials from time to time. In this page, you can find several Excel VBA examples. Click on any link to see the.
- VBA code can be defined as the code that inputs in the visual basic window to perform a set of instructions or actions in excel and provide results. With the help of VBA code, we can reduce the time to perform a repetitive task, there will not be required much human intervention except to run the program.
FreeVbCode.Com is a code repository for free Visual Basic code and samples. Visual Basic examples and articles are freely available to download and review.
1. Macro: Save All
Helpful for saving all open excel workbooks at once. It is advised to run this macro before running other macros or performing tasks that’s could potentially freeze Microsoft Excel.
Name this macro ‘SaveAll’
Example code:
2. Macro: Comments and Highlights
Helpful is you use a lot of comments and highlights while editing worksheets. Running this macro generates a new tab at the front of the worksheet with a listing of every cell with a comment or highlight in the workbook. Each cell reference is a hyperlink that leads directly to the cell with the comment/highlight. The summary tab lists the value within the cell and the text in the comment.
Additionally, there is an ‘Accept’ button that removes the highlight or deletes the comment from the chosen cell. Once all changes are accepted, the summary tab will be deleted.
NB: This macro only sets up to find certain highlights of yellow, but this can be modified.
3. Macro: Insert a Check Mark
Helpful for footing (Adding a column of numbers) trial balances, schedules and reconciliations. It is often common to put a check mark below the total to show the column total is accurate.
This macro will insert a red check mark in the active cell. Once this is added all you will be required to do is select the cell you want to check-mark in and run the macro. Name this macro ‘Checkmark’.
Example code:
4. Macro: Mail Workbook
Helpful to send a lot of excel files via email. Running this macro creates a new Microsoft Outlook email with the last saved version of the open workbook. The email, by default, will not be addressed by anyone, the subject will be the name of the workbook, and the body will be ‘See attached’. However, these settings can be customized.
Example code:
5. Macro: Copying the Sum of Selected Cells
Helpful in copying the sum of several cell in a spreadsheet. These cells can be scattered throughout the spreadsheet or all in the same row/column.
Once this macro is added you need to highlight the cells you want to sum, then run the macro, and then paste into the cell you want the sum in.
NB: This will just paste the value of the sum, not a sum() formula
Example code:
6. Macro: Open Calculator
Helpful to open a calculator.
Example code:
Sub OpenCalculator() |
7. Macro: Refresh All Pivot Tables
Helpful to refresh all pivot tables in the whole workbook in a single shot.
Example code:
8. Macro: Multiply all the Values by a Number
Helpful if you have a list of numbers you want to have multiplied by a particular number. Select the range of cells you need and run the example code below. It will first ask you for the number with whom you want to multiply and then instantly multiply all the numbers in the range with it.
Example code:
9. Macro: Add a Number to all the Numbers in Range
Similar to multiplying, you can also add a number to all the numbers in a particular range.
Example code:
10. Macro: Remove Negative Signs
Code that checks a selection and converts all the negative number into positive. Select a range and run the code.
Example code:
If you’ve done a lot of work in Excel, you’ve probably heard about Macros orVBA. Excel VBA can help you do your work much, much faster. It can also help youexpand the true power of Excel in ways you never thought possible. Ranging fromprocessing data in a worksheet all the way to scraping web pages, VBA is quitethe beast. In this post, I’d like to discuss Excel VBA for beginners. We’llcover:
- What is VBA?
- When should you use VBA?
- Getting started with the Visual Basic Editor
- Your first useful program
What is VBA and why should I care?
VBA stands forVisual Basic for Applications.It is an implementation of Microsoft’sVisual Basic 6 programminglanguage specific to Office applications in order to give you access to eachapplication’s features like cells, charts, and more. Each Office application hasits own VBA Object Model (an Object Model is sort of like a map of the featuresyou have access to with VBA). So while the VBA concepts are the same for eachOffice application, there is still a learning curve for each one.
Ok, enough with the boring stuff. Why should you care about Excel VBA?
Simple: it makes your life easier.
(You laugh - this really happened to me)
You can write programs that will do tasks for you lightning fast - leaving youmore time to do other things that are more important. This is especially usefulfor when you have to do a repetitive, tedious task to perform. For example, youcould use Excel VBA for:
- Copying and modifying data
- Apply formatting automatically
- Finding unique values
- Data checking before Saving
- Go beyond Sheet Protection
- Create forms to control data entry
- And so much more (seriously, way more)

If this article helps solve your problem, please consider supporting me because it takes a lot of effort (and coffee!) to provide this content.
👇 There's a special gift for you in return for your support.
Enjoy the post!
When Should You Use VBA?
When you have a logical, repeatable process that you do over and over, thenit’s time to consider automating it. However, if you’re just doing a one-offthing that will take you 10 minutes to do and will probably never do it again,it will probably not be worth your time making a macro to get the job done. Justrough through it. Trust me on this.
Excel VBA for Beginners - Start with the Visual Basic Editor
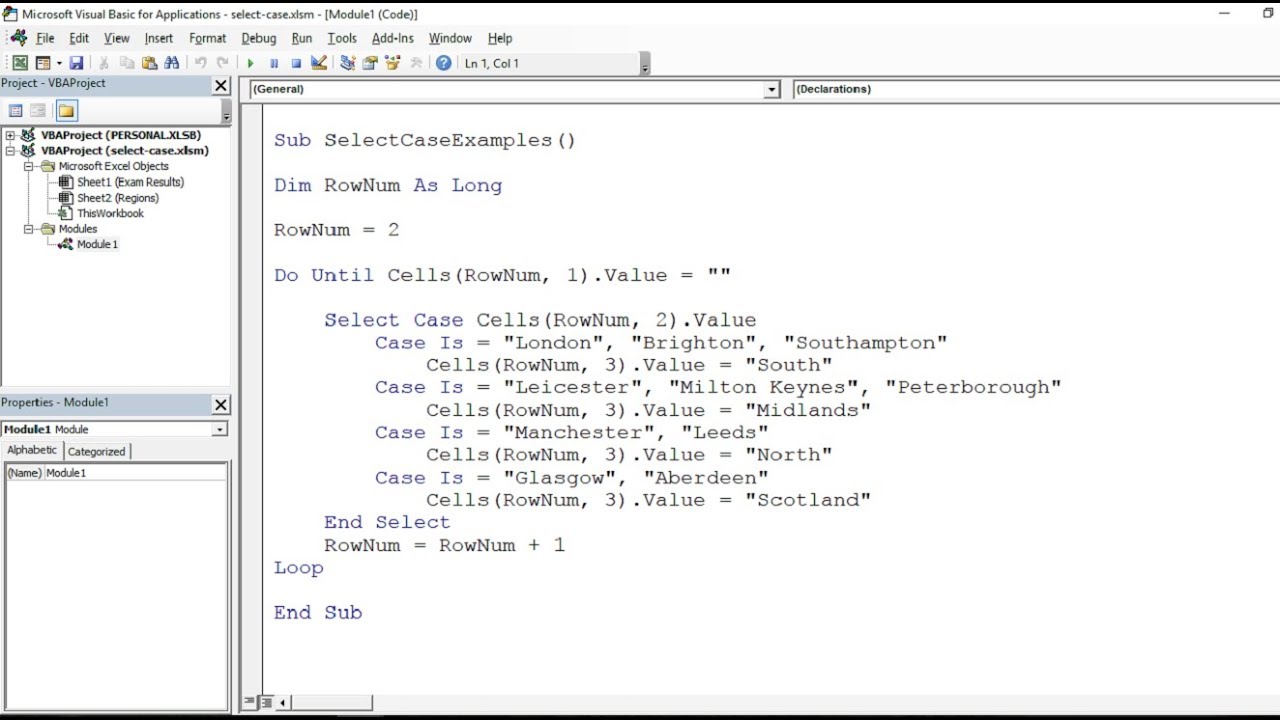
The first place to get started would be the Visual Basic Editor. PressALT+F11. You will have a new window pop up.
This is called the Visual Basic Editor and this is where you’ll be doing allyour magic. Consider this your workbench, or your garage, or your desk -whatever place you get your work done.
I’m sure you’re itching to get some coding done, and we will! But it’s importantto understand where the tools are so you understand your surroundings. So, let’squickly breakdown these components:
Excel VBA Project Window
Located at the top left of the VBE window, the Excel VBA Project window willshow you all the places where your VBA code can potentially live. Think of it asa quick reference like Windows folders in Explorer. In this section, you canfind Worksheet code, Workbook code, Userform code, regular Modules, and ClassModules. Each one of these could be considered a Project Object. All ofthese Project Objects can hold code, but each one has it’s own special uses(which I’ll cover in a later post).
Properties Window
Just below the Project Window is the Properties Window. This window holds theproperties of each Project Object that is currently selected. I haven’t foundmany times where I needed to use this, but feel free to poke around to getfamiliar with changing those properties.
Toolbar
Just your standard toolbar. We’ll dig more into this as we move along withfuture posts.
Okay. Enough of that. Let’s get to the real meat.
Writing Your First Useful Program
Many “intro to programming in X language” articles usually start with a “HelloWorld” program. What that basically means is that the article teaches you how todisplay “Hello World” to the user. But these kinds of intros leave a lot to bedesired. So, let’s forget”Hello, world!” and get someREAL work done.
Before Beginning
DANGER
Please realize that you cannot Undo any changes that Excel VBA code will maketo your spreadsheet.
Sorry, but there’s no Control+Z’ing your way out of a VBA mistake!
That said, please Save before moving executing any Excel VBA code in case somethinggoes wrong. I personally suggest that you use a test workbook when learning VBA.
For our first program, let’s delete entire rows of data if column A has aspecific value in it. For example, say we have this data:
We want to delete any row with “Delete” in it and leave the other rows alone.So, we have 4 “Keep” cells to leave alone and to delete 3 “Delete” cells. If youwere to do this, how would you begin?
Your first inclination might be to loop through the cells, search for “Delete”and, if found, delete the entire row. Yes? Cool, let’s try that.
Excel Visual Basic Programming Examples
Go to the VBE window and create a new module by right-clicking on the workbookname in the Project Window, hover over Insert, and click on Module, like so:
Add this code to the module (we’ll go over what this means in a minute):
In order to run this code:
- Go back to the workbook and select the cells A1:A8 (this is important toremember)
- Bring up the Macro Window by pressing ALT+F8
- Select “deleteText”
Click Run. Let’s take a look at the data.
…huh. There’s still one cell that says Delete.
C’mon man. How is this a useful program? It didn’t even work right!
Alright, alright. Calm down. This kind of thing is something you’ll always runinto when coding. No matter how good you get, there will always be somethingthat snags you. I figured it was a good idea to get you used to this type ofthing early on. All this means is that we have a bug in the code. So let’s”debug” it.
Debugging Code
There are a lot of debugging features to cover, but this post has already goneon and on pretty long and I want to try to hold your attention for just aliiiittle bit longer. So let’s cover the code step by step to see if we canuncover what went wrong.
The first line of code is just a variable declaration, so there’s nothing wrongwith that. The only other part of this code is the For loop, so let’s see what’sgoing on there.
This line tells VBA to process all the cells in your selection one-by-one. Inorder to do anything with the cell being processed for each time the loop runsits course, we tell VBA to assign each cell to the variable r. This is the waywe access each cell’s information as we loop through all the cells in theselection.
The text inside the cell is what we’re trying to check - and this is how wecheck it. r.Value will return whatever text is within the cell that we’reinvestigating. If the cell’s value is 'Delete' then we will move on to thenext statement, which is:
So, if the cell’s text reads “Delete” then we want to delete the entire rowthat that cell is in. Simple, right?
Well, not exactly.
When we tell VBA “hey, loop through these cells, please,” it will take thatrange of cells, and store it internally so it can loop through it. The way Exceldoes this is by using a counter to keep track of where it is within the range.So, let’s look at the original data again:
The first row has “Data” in the cell, so we skip this one. The second row has“Delete” in it, so we delete it, along with the entire row. This affects theentire range that we’re working with. So, before we deleted the row, VBA wasat row 2:
Then we delete the row, and VBA is still at row “2” (which was row 3, but isnow row 2).
What’s next in the code?
This is a way to “close off” the If statement. So only the items inside theIf statement will be executed if the If statement evaluates to True.What’s next?
This tells Excel to move to the next row down, which is row 3. So, technically,it skipped the “Keep” that was in row 3, but is now in row 2.
Confusing? Sometimes that’s just how code is :)
Microsoft Excel Visual Basic Reference
Think you know where the bug is? If you realized that the second “Delete” cellwas skipped because we modified the range while VBA was looping through it, youguessed right.
Ok, so how do we fix this?
Let’s pick something easy. Let’s find the cells that have “Delete” in them, andinstead of deleting the entire row, let’s just make the text blank. We’ll changer.EntireRow.Delete to r.ClearContents.
But that only makes the cells blank, and you want to remove the entire row forall of those. So we’ll add another line of code:
After all the “Delete” cells have had their text cleared, we do a search on theoriginal selection for blank cells, and delete the entire row for only thosecells. Here’s our new code:
Try running that code again. Notice anything different?
Awesome. Now we have working code.
Where to Go From Here
There is a lot of power in Excel VBA. When I started learning about it, I wantedto automate everything - and I practically did. I became so good at my job because Iwas getting things done faster than everyone else. This got me noticed, which was good.Then I started sharing the tools I created with my teammates and then we became fasteras a team. This got me a raise, which was better.
Visual Basic Code Excel Examples
If you continue on learning how to harness the power of VBA, it will help you outtremendously. So what are you waiting for? Let’s move on to the next item:
